Choosing the Right CMS: Joomla vs WordPress
Blogs and websites are becoming more popular by the minute. In fact, companies are not the only ones with blogs and websites. An individual also has one or both since these are helpful in establishing connection with the readers, clients or future employer. However, having a blog or website entails time and proper management.
To ensure that posts are properly placed and sites are updated regularly, companies even individuals need to use CMS or content management systems such as Joomla vs WordPress. The term content management systems may be new to some people. But this useful tool has been around for a long time and has been widely used.
In fact, since Internet was born and evolved three website construction techniques were used.
First is the Hyper Text Markup Language or HTML which involves codes. Second is the WYSIWYG (What you see is what you get) system which allows the editor to view the results while editing. Third is CMS which allows the site owner or developers to enter data easily due to the pre-set fields.

The advantage of using content management system is that it helps build and manage sites easily. For instance in organization, CMS makes documents, music, photos, text and video posting easier. There are pre-set fields that allow the user to place the data or information without dealing with codes. This also saves time since and allows the site owner to maintain it on a certain time through scheduled posts.
Moreover, CMS is also helpful in designing the overall appearance of the site through CSS or Cascade Style Sheets. This helps the developer create templates easier and faster. Lastly, CMS also offers add-ons which upgrade the functionality of a certain application. These are easy to install on a blog or website.
The CMS is indeed the easiest technique wherein an individual without html knowledge can use. In addition, the most popular CMS are Joomla vs WordPress. Though both are CMS, it is still essential to understand and know which one is right for a website.
Defining the Best
As mentioned, Joomla vs WordPress are the most popular content management systems but what are the differences between the two? Below is a detailed analysis of the two most popular content management systems.
Joomla is a free open source project released in 2005 and was upgraded and re-launched three years later. It was created by the makers of Mambo, another CMS application. This free system is mainly used for publishing and empowering various sites. It can be used for the church, community-based, corporate, e-commerce and online reservations, government applications, online media, non-profit organizations, personal, school, small business and anyone interested in developing a site.
Joomla is user-friendly and easy to install which enables the user or web developer to create and manage the site. But there are instances that the users require more features beyond the basic Joomla packages. Not to worry because there are thousands of available extensions that adds functionality for the site’s applications. Moreover, the add-ons do not only enhance the application but also extend the power of Joomla creating a better website.
With Joomla’s framework the developers are able to build and manage application bridges and communication tools. In addition, Joomla can also help manage complex business directories, custom product catalogs as well as data reporting tools. But it does not end there, integrated e-commerce systems, inventory control and reservation systems are also included.
WordPress, on the other hand, is the newest version of b2/cafelog. This free open source project was developed in 2001 and was released in 2003. From enhancing a simple typography for a number of users, it has grown in to a bigger and powerful blogging tool used by millions.
Though the CMS started as a blogging tool, it is actually more than that. It can also be used as a full content management system where users can explore and choose thousands of themes and plugins available. Moreover, there are also widgets that can be dragged and dropped on the page. Users can also include social media sites to be able to share the content easily.
Furthermore, WordPress is also a multi-user and multi-blogging platform. Prior to WordPress 3.0, there was WordPress MU. To enhance the features and offer something new, but both were merged later on. Besides that, WordPress.org also brought in WordPress.com so that that a larger audience will be able to experience a hosted version. This version also has thousands of themes, plug-ins as well as widgets.
Joomla vs WordPress
There is a tight competition between the two best CMS in the world. As written above, both are useful tools for websites; however, both still differ from each other.
Joomla is excellent in managing and maintaining e-commerce and professional sites because it offers the right features for adding and updating images, pages and navigation menus. It also increases functionality of a website due to extensions and provides flexibility in design a website.
Meanwhile, WordPress is ideal for bloggers because it is easy to install and use. It can be customized accordingly due to the easy to install plug-ins making the site dynamic. In addition, it also allows and posts comments automatically.
These show that both CMS caters to different audiences. Moreover, both also differ in terms of how easy an individual will get the hang of it. Between Joomla vs WordPress, WordPress is more user-friendly, quick and at the same time classy.
First, though both are PHP / MySQL based WordPress uses less server resources and less codes. This enables the site to load and display faster. In addition, the site owner can easily and quickly publish data or information. Second, WordPress themes can be installed easily and are adaptive. This means that the site displays different resolutions depending on the device used.
Third, creating and publishing content is extremely easy in WordPress. There is no need to be knowledgeable in codes or other programs. Fourth, WordPress is good in SEO. Due to the plug-ins, themes and other features, WordPress is able to balance the contents making the pages light and SEO friendly. This also helps in raising traffic and in good site ranking. Lastly, it is more fun creating and managing a website in WordPress because it gives the user everything he needs.
 MySQL is the most famous open-source database system on the World Wide Web. MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores both data and the data’s relationships on the same table. Asides from that, a user can reassemble and access its data in many ways without the need of creating any changes to the tables. With MySQL, you can create up to 4,096 columns and store an almost unlimited number of records.
MySQL is the most famous open-source database system on the World Wide Web. MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores both data and the data’s relationships on the same table. Asides from that, a user can reassemble and access its data in many ways without the need of creating any changes to the tables. With MySQL, you can create up to 4,096 columns and store an almost unlimited number of records.

 This language is capable of running scripts for a server, and it can carry out specific server tasks. Few of the common tasks it can perform are database manipulation and content management. The scripts will be saved on the server just like the web pages, and they will only be triggered when users request it to be executed.
This language is capable of running scripts for a server, and it can carry out specific server tasks. Few of the common tasks it can perform are database manipulation and content management. The scripts will be saved on the server just like the web pages, and they will only be triggered when users request it to be executed.

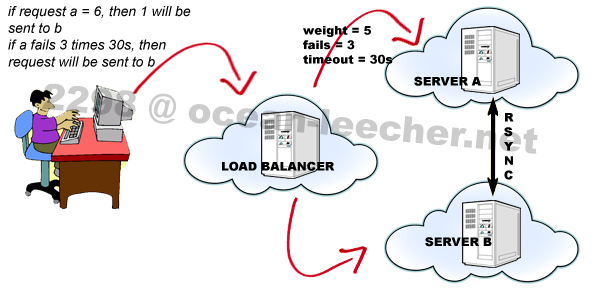
 First, you would need a computer server, which is either your own computer or one from a
First, you would need a computer server, which is either your own computer or one from a  First, you have to backup your hosting files because you have to expect inevitable events. Your service provider could experience technical difficulties or a server crash that could wipeout your data temporarily or permanently. Although this is rare in most cases, it does happen in reality. When you read hosting reviews, take note of the details concerning the provider’s redundant power sources, backup generators and data center.
First, you have to backup your hosting files because you have to expect inevitable events. Your service provider could experience technical difficulties or a server crash that could wipeout your data temporarily or permanently. Although this is rare in most cases, it does happen in reality. When you read hosting reviews, take note of the details concerning the provider’s redundant power sources, backup generators and data center.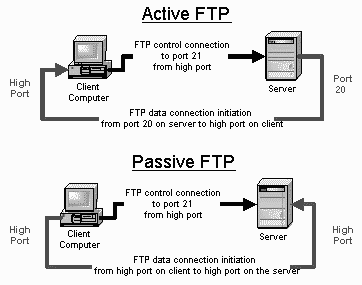 Second, when you open your chosen FTP Client, you have to enter the host name (that is, “ftp” followed by your domain name), your username and password and port (usually, no. 21), or simply log in anonymously. You would have to create an account to authorize yourself or others in order to access a hosting server. An important FTP security tip, though, is to use new username and password because your details and file contents are sent in clear text, which can be intercepted by packet sniffers and eavesdroppers.
Second, when you open your chosen FTP Client, you have to enter the host name (that is, “ftp” followed by your domain name), your username and password and port (usually, no. 21), or simply log in anonymously. You would have to create an account to authorize yourself or others in order to access a hosting server. An important FTP security tip, though, is to use new username and password because your details and file contents are sent in clear text, which can be intercepted by packet sniffers and eavesdroppers.