Website: http://vpsblast.net
System Information
 (more…)
(more…)
{ 0 comments }
{ 0 comments }
Okay we continue to the third part of this post title, on the previous part we use NginX as load balancer and failover, now we use NginX with Geo IP based to determine the best backend for the visitors to put, here is the illustration.

For instance, we have two backend servers located in UK and DE, then we put the visitors from United Kingdom to the UK backend, visitors from Germany to DE backend, and the rest will be divided into those two backend servers, let’s deal with it.
I assume you have installed NginX in your frontend and two backend servers, you can check the previous post for NginX installation. This GeoIP based location needs GeoIP database for the frontend server to determine where to put the visitor, so first we download and extract Lite version of GeoIP database from Maxmind with geo2nginx.pl script from http://markmaunder.com.
wget https://serversreview.net/pkgs/txt/geo2nginx.pl chmod 755 geo2nginx.pl wget http://geolite.maxmind.com/download/geoip/database/GeoIPCountryCSV.zip unzip GeoIPCountryCSV.zip ./geo2nginx.pl < GeoIPCountryWhois.csv > geo.conf mv geo.conf /etc/nginx/
GeoIP database has been added to NginX directory, now to the configuration, here is the example of main configuration
{ 0 comments }
On the previous post we were talking about simple dns failover using two nameservers / ip addresses, now we will move the conversation to the more exciting one, we will use frontend server to control the backend servers, here is the illustration.
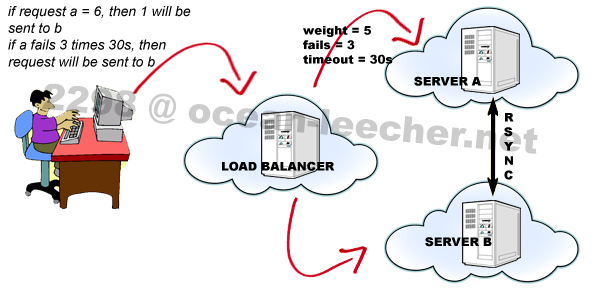
One frontend server decides whether to put the visitor to the server A or server B, here i am using NginX as frontend and also NginX as backend server.
Why don’t you use another web server as the backend?
I like NginX, for me it is easy to understand NginX configuration than another web server. Before we start to configure it, install NginX on the frontend and backend servers. I’m using CentOS 5 by the way.
wget http://pkgs.serversreview.net/files/nginx-1.1.13.tar.gz tar -zxvf nginx-1.1.13.tar.gz cd nginx-1.1.13 useradd www passwd www ./configure --prefix=/usr --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ --user=www --group=www --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_perl_module --with-mail --with-file-aio --with-mail_ssl_module --with-ipv6 make make install
in the configurations above, as usual i am using “www” user and group for NginX. Next download NginX init script and make it executable.
{ 0 comments }
Yeah guys, let’s talk about this post title, really it is interesting, i mean for me this is very interesting :p. If you have a site, and then something happen to your server’s network, and unfortunately your site does not have backup or mirror site which is very essential because your site is your income. So the first thing you need to do is this, do not put your site in shared / reseller hosting. Why? Because in shared hosting, your site is not alone, there are so much neighbor in it, and your site could be exploited from those neighbor, for instance bug in script. Another thing is you cannot get root access from shared hosting, your creativity is limited by non-ssh regular user assigned to your account. So take a look at LowEndBox and get a vps for your shared hosting substitution.
Nuff said for the appetizer, let’s get to the main course. The simplest failover method for website is round robin dns, the illustration would be like this:

where the server has been assigned with two or more ip addresses, so if end user fail to access the server with the first ip address, it will be routed to the second ip address. To use that settings, you simply
{ 0 comments }
{ 0 comments }
Most of shared / reseller hosting providers that use cPanel as their control panel must have this order in their cPanel structure.
Example one Server with one IP address using cPanel
cPanel root / super user -> master reseller -> reseller -> shared
further down that many users / domains would use the ip
also cPanel shared hosting usually creates user directory under /home directory, so normally it will be hundreds of user directory right? but the screenshot says different, there is only one user directory
and when I up to directory above /home, there is no root directory
It is a little bit odd right? Yes and so it is called jailed SSH.
Basically, jailed ssh creates a shell scene within a particular directory where your shell activities locked in there. This intended to locked you into that directory instead of you being able to go freely to any other directories, something like ftp server does restrict you to your home directory. Also system administrator or host can decide or restrict what command or program can run in the jailed shell scene, usually they are disabling super user commands, so only basic shell command allowed to run in the jailed ssh.
{ 0 comments }
{ 0 comments }
{ 0 comments }
Even though most of PHP applications is now running with PHP version 5.3, there are a few PHP applications are still running on PHP version 5.2, you can see what makes that thing happens here: http://php.net/manual/en/migration53.incompatible.php
So i guess it will be good for PHP programmer / developer to have PHP version 5.2 and 5.3 installed and running on the same machine (more economical than using two machines for each PHP version). So let’s get started.
Anyway i will use NginX as the webserver, so the main principle of two PHP version running on the same machine is CGI works using different localhost port.
Before installing PHP, we usually install webserver and database first, i assume that you all have installed NginX and MySQL, so i just skip to the PHP installation.
note: the configuration below is my usual config and dependencies, if you are experiencing error while configure or make php, try to find out about the missing dependencies by looking at this blog’s older posts or googling. The first four configuration of PHP will be the important note because we will separate PHP 5.3 and 5.2 configuration (php.ini) path.
--prefix=/usr/local53 --libdir=/usr/local53/lib --with-libdir=lib --with-config-file-path=/usr/local53/lib --prefix=/usr/local52 --libdir=/usr/local52/lib --with-libdir=lib --with-config-file-path=/usr/local52/lib
Install PHP 5.3.8 with PHP-FPM
wget http://pkgs.serversreview.net/files/autoconf-2.13.tar.gz tar -zxvf autoconf-2.13.tar.gz cd autoconf-2.13 ./configure make && make install wget http://pkgs.serversreview.net/files/php-5.3.8.tar.gz tar -zxvf php-5.3.8.tar.gz cd php-5.3.8 ./buildconf --force ./configure --prefix=/usr/local53 --libdir=/usr/local53/lib --with-libdir=lib --with-config-file-path=/usr/local53/lib --enable-force-cgi-redirect --enable-fpm --enable-cli --with-mcrypt --enable-mbstring --with-openssl --with-mysql=/usr/local/mysql --with-mysqli=/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_config --with-mysql-sock=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock --with-pdo-mysql=/usr/local/mysql --with-gd --with-zlib --with-jpeg-dir=/usr/lib --with-png-dir=/usr/lib --with-png --with-jpeg --with-gmp --with-sqlite --enable-pdo --with-xpm-dir=/usr/lib --with-freetype-dir=/usr/include/freetype2 --with-ttf=/usr/include/freetype2 --enable-gd-native-ttf --enable-fileinfo --disable-debug --with-pic --with-bz2 --with-curl --with-curlwrappers --without-gdbm --with-gettext --with-iconv --with-pspell --with-pcre-regex --with-imap --with-imap-ssl=/usr/lib --enable-exif --enable-ftp --enable-magic-quotes --enable-sockets --disable-sysvsem --disable-sysvshm --disable-sysvmsg --enable-track-vars --enable-trans-sid --enable-yp --enable-wddx --with-kerberos --enable-ucd-snmp-hack --enable-memory-limit --enable-shmop --enable-calendar --enable-dbx --enable-dio --with-mime-magic --with-system-tzdata --with-odbc --enable-gd-jis-conv --enable-dom --disable-dba --enable-xmlreader --enable-xmlwriter --with-tidy --with-xml --with-xmlrpc --with-xsl --enable-bcmath --enable-soap --enable-zip --enable-inline-optimization --with-mhash --enable-mbregex make make install cp php.ini-production /usr/local53/lib/php.ini
{ 0 comments }